Types of Cabinet Door Parts: Cabinet Door Parts Names

Cabinet doors, seemingly simple components, are comprised of a variety of parts working in concert to create functional and aesthetically pleasing storage solutions. Understanding these individual components is crucial for both DIY enthusiasts and professionals alike, allowing for efficient repairs, replacements, and informed purchasing decisions. This section details the common parts, their functions, and potential issues.
Cabinet Door Parts Table
Understanding the various parts of a cabinet door is essential for effective repair, replacement, and overall cabinet maintenance. The following table provides a comprehensive overview of common components, their functions, typical materials, and potential problems.
| Part Name | Function | Material | Common Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Door Panel | The visible surface of the door; provides the aesthetic appeal. | Wood (solid wood, plywood, MDF), glass, metal, plastic laminate | Scratches, dents, warping, delamination (in laminated doors) |
| Frame (for framed doors) | Provides structural support and defines the door’s shape. | Wood (solid wood, hardwood), MDF | Cracking, warping, joint failure |
| Rails (for framed doors) | Horizontal members of the frame. | Wood (solid wood, hardwood), MDF | Cracking, warping |
| Stiles (for framed doors) | Vertical members of the frame. | Wood (solid wood, hardwood), MDF | Cracking, warping |
| Hinges | Connect the door to the cabinet frame, allowing for opening and closing. | Metal (steel, brass, zinc alloy) | Sagging, loosening, corrosion |
| Cabinet Door Knobs/Pulls | Provide a grip for opening and closing the door. | Metal (various alloys), ceramic, plastic, wood | Loose screws, breakage, tarnishing |
| Insert (for inset doors) | A panel that fits within the frame of an inset door. | Wood (solid wood, plywood, MDF), glass | Warpage, loose fit |
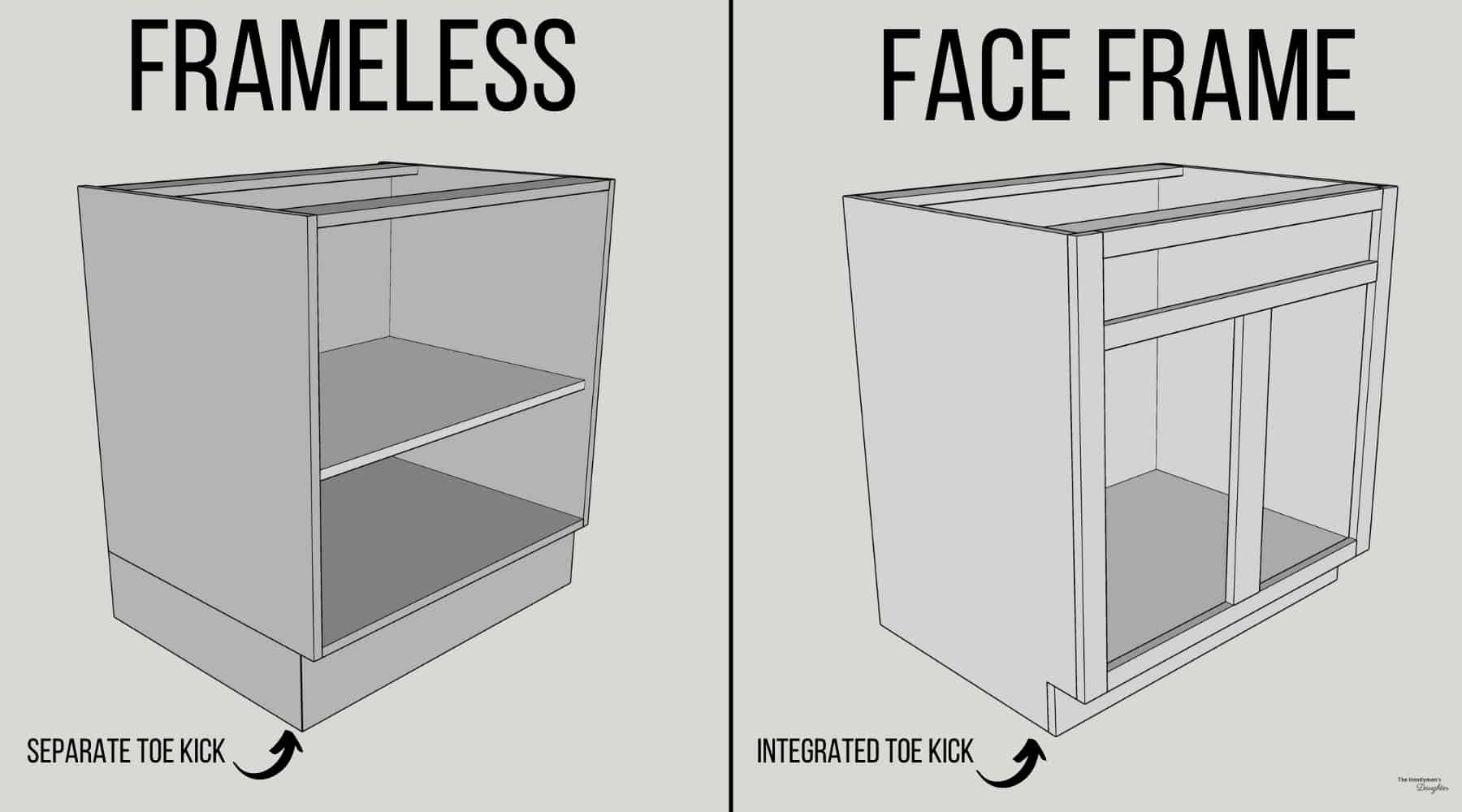
Frameless vs. Framed Cabinet Doors
The fundamental difference between frameless and framed cabinet doors lies in their construction. This impacts both the aesthetic and the structural integrity of the cabinet.
Cabinet door parts names – The following points highlight the key distinctions:
- Frameless Doors: These doors consist of a single panel, often with a simple edge profile. They are generally more modern in appearance and offer a clean, minimalist aesthetic. They rely on the strength of the panel itself and the hinges for support.
- Framed Doors: These doors feature a frame (rails and stiles) that encloses a panel. This frame provides additional structural support, making them more durable, especially for larger doors. They often have a more traditional look.
- Unique Parts: Frameless doors lack rails and stiles, which are defining features of framed doors. Framed doors require additional components for assembling the frame and attaching the panel.
- Installation: Frameless doors typically use full overlay hinges, while framed doors can utilize full overlay, partial overlay, or inset hinges depending on the desired look and functionality.
- Cost: Generally, frameless doors are slightly more expensive due to the need for higher-quality materials and precision manufacturing to maintain structural integrity without a frame.
Cabinet Door Hinge Variations, Cabinet door parts names
Hinges are crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of cabinet doors. Different hinge types offer varied aesthetics and functionality.
Three primary hinge types are commonly used:
- Overlay Hinges: These hinges allow the door to overlap the cabinet frame. Full overlay hinges cause the door to completely cover the frame, while partial overlay hinges leave a portion of the frame visible. An illustration of a full overlay hinge would show two hinge cups (one mounted on the door and one on the cabinet frame), connected by a hinge pin, allowing for a 180-degree opening. The hinge cups would be positioned so that the door completely covers the cabinet frame when closed. A partial overlay hinge would show a similar configuration but with the cups positioned to leave a visible portion of the cabinet frame.
- Inset Hinges: Inset hinges are used when the cabinet door sits flush within the cabinet frame. An illustration would depict hinges that are concealed within the frame and door, allowing the door to sit completely recessed. The hinges would likely be mortised into both the door and the frame, requiring precise placement and fitting.
Identifying and Troubleshooting Cabinet Door Problems
Cabinet door malfunctions are common household annoyances, ranging from minor inconveniences to significant repairs. Understanding the root causes and employing effective troubleshooting techniques can save time, money, and frustration. This guide provides practical solutions for resolving frequent cabinet door issues, empowering homeowners to tackle these problems confidently.
Troubleshooting Common Cabinet Door Issues
Addressing cabinet door problems effectively requires a systematic approach. Identifying the specific issue is the first step towards a successful repair. The following list Artikels common problems and their potential causes.
- Sticking Doors: This often stems from swelling wood due to humidity, paint buildup, or warped door frames. Check for obstructions, misaligned hinges, or warped door panels.
- Loose Hinges: Over time, screws can loosen, causing doors to sag or become unstable. This is usually caused by repeated opening and closing or insufficiently tight screws during installation.
- Damaged Panels: Impacts, scratches, and general wear and tear can damage cabinet door panels. This might involve chips, cracks, or significant dents.
- Misaligned Doors: Doors that don’t close properly or gap unevenly indicate alignment issues. This can result from loose hinges, improperly installed doors, or warped cabinet frames.
- Faulty Latches or Catches: Problems with door latches or catches can prevent doors from closing securely. This might be due to broken components, misalignment, or wear and tear.
Repairing and Replacing Cabinet Door Parts
Repairing or replacing damaged cabinet door parts is often a straightforward process. The following steps Artikel common repairs, providing visual descriptions to guide the process.
- Replacing Loose Hinges:
- Visual Description: Imagine a hinge with loose screws. The screw holes might be stripped or the wood surrounding them may be weakened.
- Remove the loose hinge. Carefully pry it off the door and cabinet frame.
- If the screw holes are stripped, fill them with wood filler, allowing it to dry completely. Then, re-drill pilot holes for new screws.
- Attach the hinge to the door and cabinet frame using new screws, ensuring they are firmly tightened.
- Replacing Knobs and Handles:
- Visual Description: A knob or handle that is loose or broken. The mounting screw might be missing or stripped.
- Remove the old knob or handle. Usually, this involves unscrewing a retaining nut or screw from the back of the door.
- Install the new knob or handle, ensuring it is securely fastened with the appropriate screws.
- Repairing Damaged Panels: Minor scratches can be repaired with wood filler and sanding. More significant damage might require replacement of the entire panel.
Methods for Adjusting Cabinet Door Alignment
Proper cabinet door alignment ensures smooth operation and an aesthetically pleasing appearance. Several methods can achieve this.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Adjusting Hinge Screws | Tightening or loosening hinge screws can subtly adjust the door’s position. This is best for minor misalignments. Experiment with adjusting screws individually to achieve optimal alignment. |
| Shim Placement | Placing thin shims (small pieces of wood or metal) between the cabinet frame and the door can correct alignment issues. Shims are particularly useful for uneven gaps between the door and frame. |
| Hinge Repositioning | If the alignment problem is significant, the hinges may need to be repositioned entirely. This involves removing the hinges and drilling new pilot holes to adjust the door’s placement. |
| Cabinet Frame Adjustment | In cases where the cabinet frame itself is warped or uneven, adjustments to the frame may be necessary. This is a more complex procedure, potentially requiring woodworking skills or professional assistance. |
Cabinet Door Styles and Design Elements

Cabinet doors are more than just functional components; they significantly impact a room’s overall aesthetic. The style of your cabinet doors, combined with the choice of materials and hardware, can transform a kitchen or bathroom from ordinary to extraordinary. Understanding the various styles and the elements that define them is crucial for achieving the desired look.
Shaker Style Cabinet Doors
Shaker style cabinet doors are characterized by their simple, clean lines and timeless appeal. They feature a recessed center panel framed by a raised frame. This creates a subtle yet elegant look that suits a wide range of design styles.
Key Design Feature: The recessed center panel, framed by a simple, flat raised frame, is the defining characteristic of a Shaker door. The overall effect is one of understated elegance and functionality.
Flat Panel Cabinet Doors
Flat panel doors are exactly as their name suggests: a single, flat panel without any raised or recessed features. This minimalist style is modern and sleek, perfect for contemporary kitchens and bathrooms. The absence of ornamentation allows the material and finish to take center stage.
Key Design Feature: The completely flat surface of the door is the defining characteristic. This style emphasizes clean lines and a minimalist aesthetic.
Raised Panel Cabinet Doors
Raised panel doors showcase a raised center panel, creating a three-dimensional effect. This classic style adds visual interest and texture, offering a more traditional and ornate look than flat panel or Shaker doors. The raised panel can be simple or elaborate, depending on the design.
Key Design Feature: The prominent raised center panel is the defining feature, providing depth and visual interest. The style of the raised panel itself can vary widely.
Beaded Inset Cabinet Doors
Beaded inset doors feature a recessed center panel with decorative beading along the edges. This creates a more ornate and traditional look compared to Shaker or flat panel doors. The beading adds a touch of elegance and detail, making it a popular choice for classic or transitional kitchens.
Key Design Feature: The recessed panel with decorative beading around the edges gives this style a classic and refined appearance.
Cabinet Door Parts and Their Contribution to Aesthetic
The overall aesthetic of a cabinet door is a result of the interplay of various parts. Understanding these parts helps in appreciating the design and making informed choices.
| Style | Key Parts | Visual Description |
|---|---|---|
| Shaker | Frame, Panel, Stiles, Rails | A recessed center panel is framed by a raised border, creating a simple yet elegant look. The frame is usually flat. |
| Flat Panel | Single Panel | A single, flat panel without any raised or recessed features. Clean and minimalist in appearance. |
| Raised Panel | Panel, Rails, Stiles | A raised center panel sits within a frame, adding depth and visual interest. The raised panel can be subtly or dramatically raised. |
| Beaded Inset | Panel, Rails, Stiles, Beading | A recessed panel with decorative beading around the edges. The beading adds a touch of elegance and detail. |
